02 Sep 2009: Enterprise Linux 5.3 to 5.4 risk report
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4 was released today, just over 7 months since the release of 5.3 in January 2009. So let's use this opportunity to take a quick look back over the vulnerabilities and security updates we've made in that time, specifically for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Server.Errata count
The chart below illustrates the total number of security updates issued for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 Server as if you installed 5.3, up to and including the 5.4 release, broken down by severity. I've split it into two columns, one for the packages you'd get if you did a default install, and the other if you installed every single package (which is unlikely as it would involve a bit of manual effort to select every one). For a given installation, the number of package updates and vulnerabilities that affected you will depend on exactly what you have installed or removed.
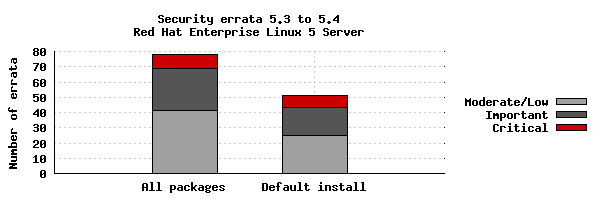
So for a default install, from release of 5.3 up to and including 5.4, we shipped 51 advisories to address 166 vulnerabilities. 8 advisories were rated critical, 18 were important, and the remaining 25 were moderate and low.
Or, for all packages, from release of 5.3 to and including 5.4, we shipped 78 advisories to address 251 vulnerabilities. 9 advisories were rated critical, 28 were important, and the remaining 41 were moderate and low.
Critical vulnerabilities
The 9 critical advisories were for just 3 different packages. In all the cases below, given the nature of the flaws, ExecShield protections in RHEL5 should make exploiting these memory flaws harder.
- Seven updates to Firefox (February, March 4th, March 27th, April 21st, April 27th, June, July ) where a malicious web site could potentially run arbitrary code as the user running Firefox.
- An update to kdelibs (June), where a malicious web site could potentially run arbitrary code as the user running the Konqueror browser. kdelibs is not a default installation package.
- An update to the NSS library (July), where a service could present a malicious SSL certificate causing a heap overflow which could potentially run arbitrary code as the user running a browser such as Firefox.
Updates to correct all of these critical vulnerabilities were available via Red Hat Network either the same day, or up to one calendar day after the issues were public.
In fact for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 since release and to date, every critical vulnerability has had an update available to address it available from the Red Hat Network either the same day or the next calendar day after the issue was public.
Other significant vulnerabilities
Although not in the definition of critical severity, also of interest during this period were several NULL pointer dereference kernel issues. NULL pointer dereference flaws in the Linux kernel can often be easily abused by a local unprivileged user to gain root privileges through the mapping of low memory pages and crafting them to contain valid malicious instructions:
- CVE-2009-2698 was public on August 24th and a working privilege escalation exploit was published about a week later. This issue was addressed for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 by a kernel update on August 24th.
- CVE-2009-2692 was public on August 13th and a working privilege escalation exploit was published the same day. This issue was addressed for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 by a kernel update on August 24th.
- CVE-2009-1897 was public on July 16th along with a working privilege escalation exploit. This issue affected only beta versions of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4 kernel and it was addressed prior to the release of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.4.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux since 5.2 has contained backported patches from the upstream Linux kernel to add the ability to restrict unprivileged mapping of low memory, designed to mitigate NULL pointer dereference flaws. However it was found that this protection was not sufficient, as a system with SELinux enabled is more permissive in allowing local users in the unconfined_t domain to map low memory areas even if the mmap_min_addr restriction is enabled. This is CVE-2009-2695 and will be addressed in a future kernel update.
Mitigations
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 shipped with a number of security technologies designed to make it harder to exploit vulnerabilities and in some cases block exploits for certain flaw types completely. From 5.3 to 5.4 there were three flaws blocked that would otherwise have required critical updates:
- CVE-2009-0692, a stack buffer overflow flaw in dhclient. FORTIFY_SOURCE protection detects the overflow and causes dhclient to exit with no security consequence. No security update for users of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5 was needed.
- CVE-2009-1252 a buffer overflow flaw in NTP caught by FORTIFY_SOURCE. We issued an update as a remote attacker could still cause a denial of service.
- CVE-2009-0846, a uninitialized pointer free in krb5. glibc provides a hardened malloc/free implementation which mitigates the exploitability of this flaw, however we issued an update as a remote attacker could still cause a denial of service.
Previous updates
To compare these statistics with previous update releases we need to take into account that the time between each update is different. So looking at a default installation and calculating the number of advisories per month gives the results illustrated by the following chart:
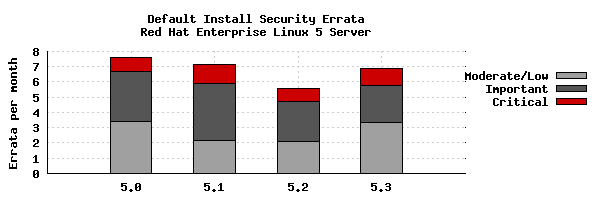
This data is interesting to get a feel for the risk of running Enterprise Linux 5 Server, but isn't really useful for comparisons with other versions, distributions, or operating systems -- for example, a default install of Red Hat Enterprise Linux 4AS did not include Firefox, but 5 Server does. You can use our public security measurement data and tools, and run your own custom metrics for any given Red Hat product, package set, timescales, and severity range of interest.
See also: 5.2 to 5.3, 5.1 to 5.2, and 5.0 to 5.1 risk reports.
Created: 02 Sep 2009
Tagged as: cve, fedora, metrics, red hat, security
